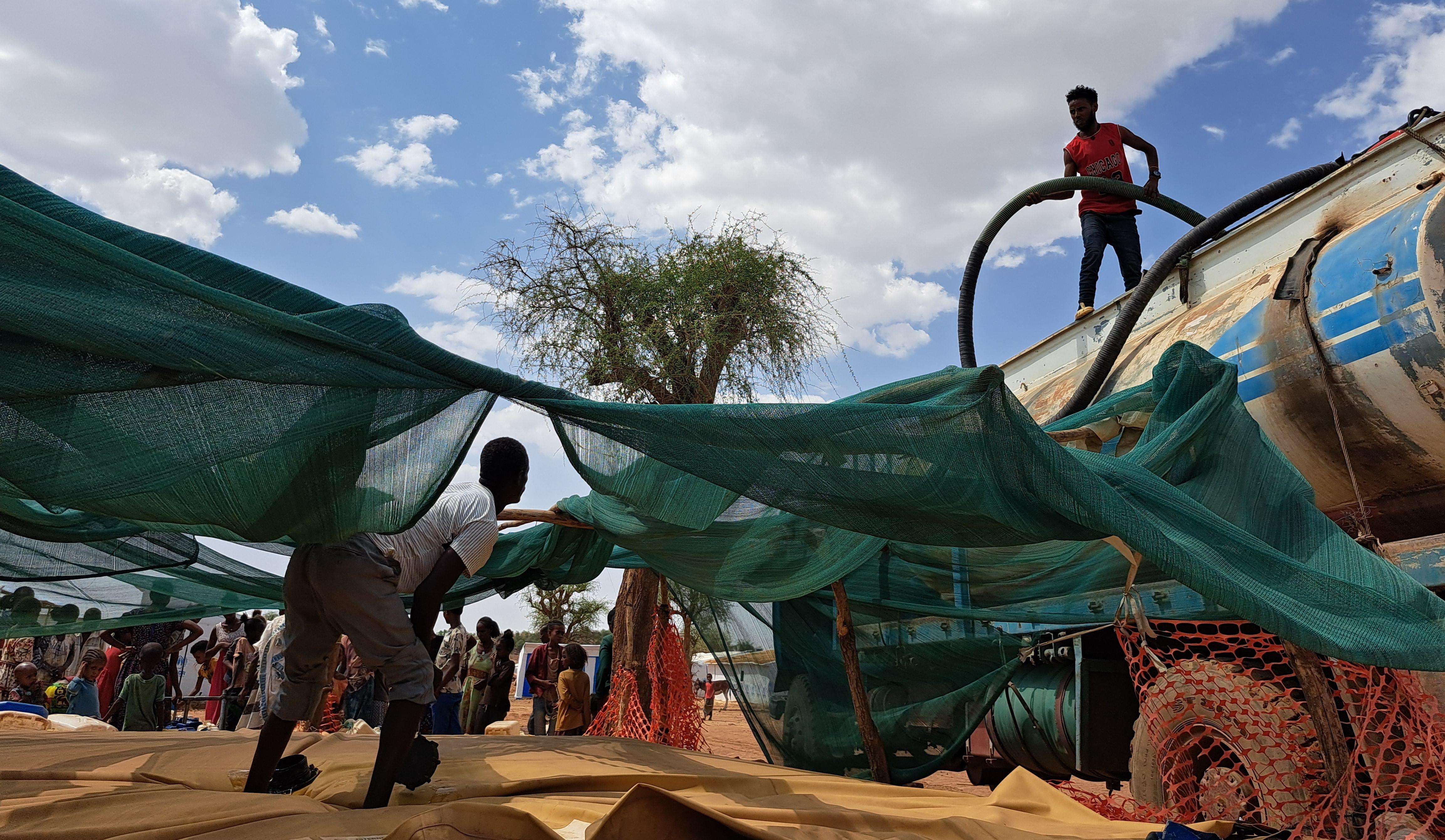
“I’m the water man,” says Weldekiros Assefa, an engineer and water and sanitation expert for Doctors Without Borders/Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) in Ethiopia. “I have the best job at MSF.”
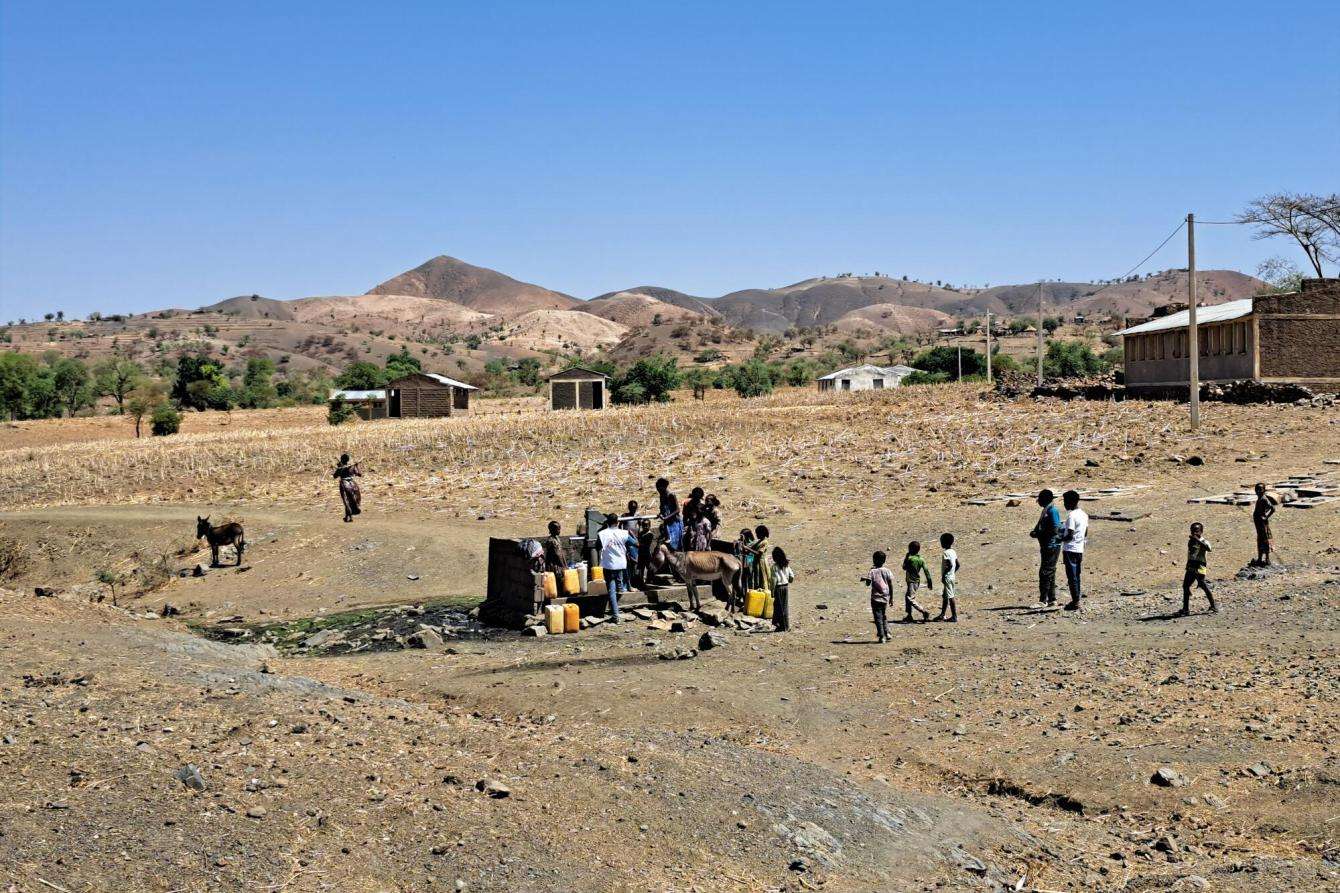
Assefa is checking water hand pumps in May Kwait, a small village in northwestern Tigray, a region in Ethiopia where 600 hand pumps are working again after being repaired with the help of MSF. The repaired pumps restore access to clean water in a place where—not long ago—water was scarce to non-existent during two years of civil war.
“When the fighting got really bad here, people fled into the forest for a week,” Assefa explains. “When they returned, the electricity had been cut off and the water hand pumps that many rely on for water had been dismantled and filled with stones.” They were the last working pumps in the area.
The people of May Kwait were left with no choice but to walk almost a mile to fetch water from the river. Many became ill with diarrhea. Whatever water people had was mainly used for cooking and drinking, but not for washing—increasing the risk of skin diseases and other illnesses that spread rapidly without access to hygiene.


From left: Weldekiros Assefa checks a hand pump for repairs in the village of May Kwait; damage to Sheraro health center from a blast in civil war. Ethiopia 2023 © Gabriella Bianchi/MSF
MSF returns to Tigray
When MSF teams were able to return to Tigray in November 2022, the region was emerging from a devastating two-year civil war. The war caused significant damage to infrastructure, whether due to lack of maintenance, intentional destruction, or the fighting. Health facilities were hardly functioning.

Ethiopia: MSF forced to suspend majority of activities amid enormous needs
Read moreAmong MSF’s first priorities was rehabilitating health facilities’ water systems and re-establishing a functioning waste management system. In Shire’s Suhul hospital, for instance, the team managed to get safe water flowing again and built latrines, showers, and areas for washing. They also installed incinerators to ensure safe disposal of medical waste. Most crucially, the team cleared a mountain of rubbish containing hazardous medical waste close to the facility.
Another critical goal was to bring safe water into people’s homes to prevent the spread of diseases spread by river water, including acute watery diarrhea, skin and eye diseases, and those caused by parasites. The biggest fear was that the lack of access to clean water might trigger a cholera outbreak.
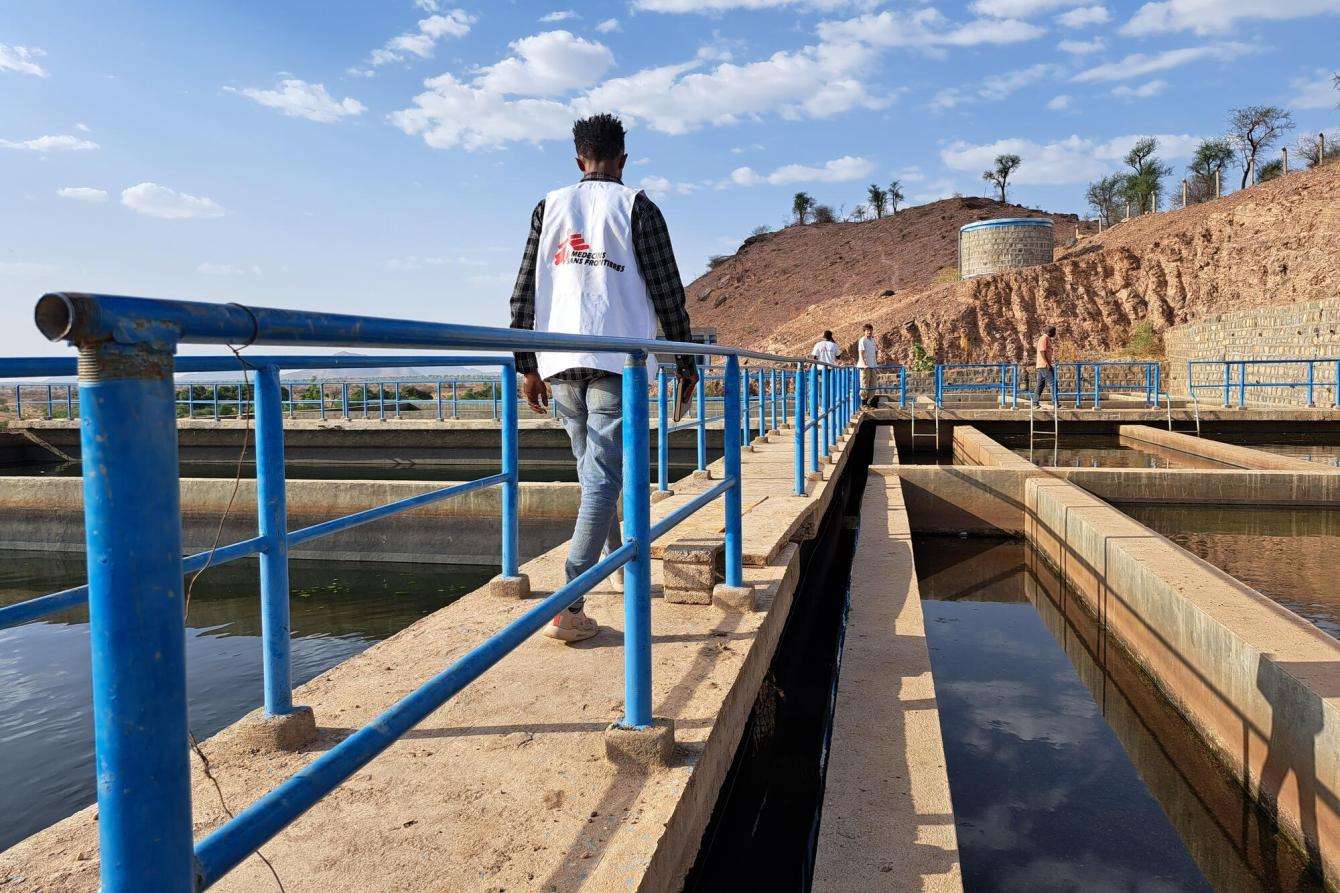

Medical consequences of living without water and sanitation
Between December 2022 and March 2023, several assessments were done in northwestern and central Tigray and showed that only 34 percent of water hand pumps were still functioning among the 2,000 surveyed across 14 districts. It was critical to repair the unusable pumps ahead of the rainy season, when water sources can become contaminated from open defecation, increasing the risk of cholera outbreaks.
When water hand pumps aren’t functioning, people will use water from lakes and rivers, which is often unsafe. “At one stage, towards the end of March, almost one in four ambulatory patients we were seeing in Tigray were suffering from preventable waterborne diseases,” says Samreen Hussain, MSF medical coordinator in Ethiopia.

Ethiopia 2023 © Gabriella Bianchi/MSF
— Hedat
At the end of April, several cases of acute watery diarrhea were recorded in Derso, a small village south of Sheraro, after a 10-year-old boy died on his way to a rural health facility. “The conditions in the village were very poor,” says Daniel Shmondi, an MSF water and sanitation supervisor who was among the team assessing the situation in the area. “There were no wells and people were using water from the river for all purposes.” A lack of toilets also raised the risk of disease outbreaks.
In response, the team distributed water purification tablets to 120 households and checked whether other people in the village had become sick. They found that two siblings of the boy who died had severe diarrhea, and they were then admitted to an isolation center that MSF helped set up in Sheraro to prepare for a possible cholera outbreak. This also triggered a response at Suhul Hospital, the referral facility for the region, which is two-hour drive away. The hospital rehabilitated its cholera treatment center and trained staff to strengthen their ability to respond during outbreaks.
Persistent insecurity slows recovery
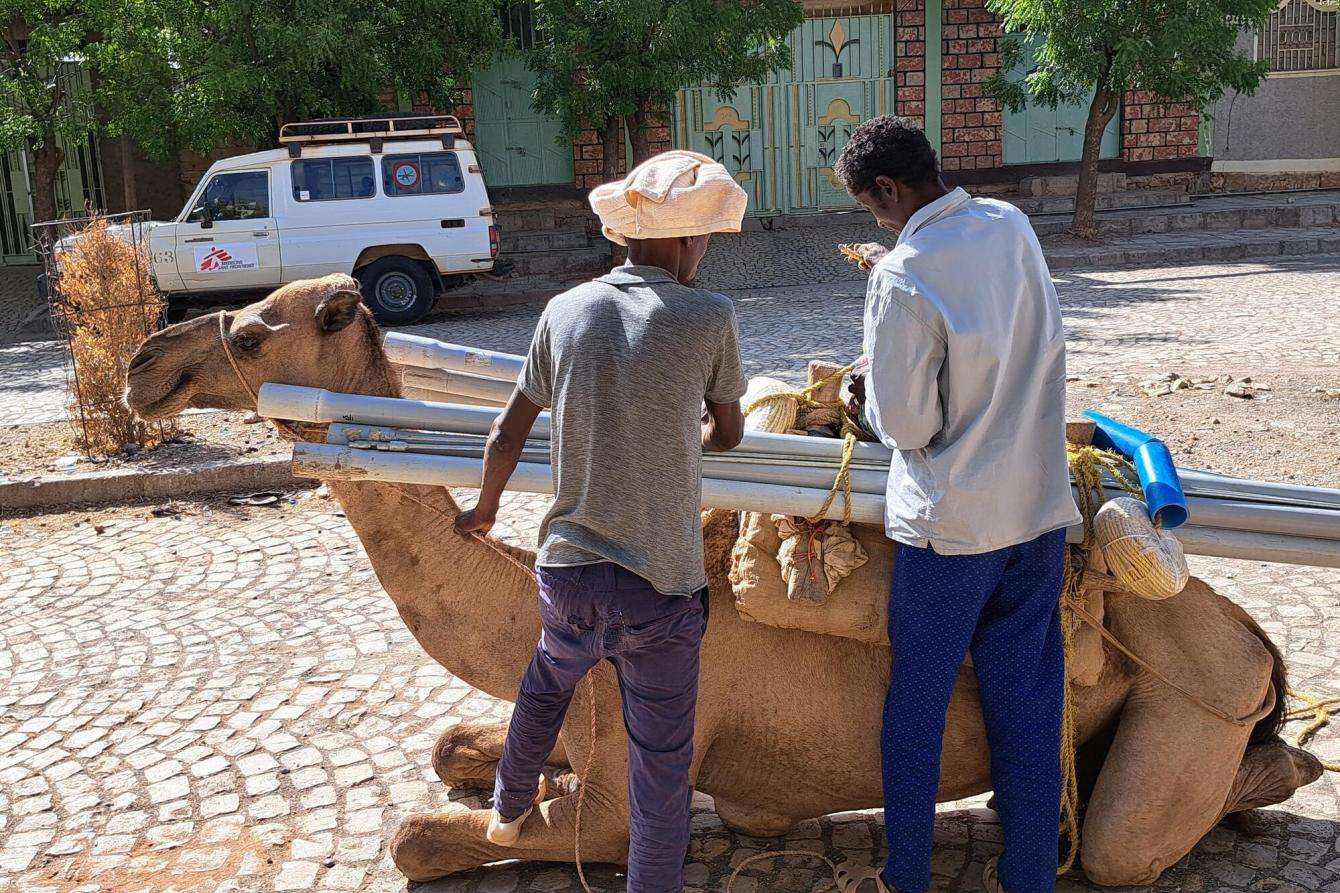
Early in the morning, Adisalem loads his camel with the spare parts he will need to repair a hand pump in Ademeyti, a village at the border with Eritrea. “In this area most people have not returned yet,” he says. “Many are still living in camps or with hosts in the community.”
Persisting insecurity has also slowed down recovery from the war. Water infrastructure in Tigray underwent costly repairs several times, only to be looted or intentionally destroyed again.

Aid organizations have been hesitant to carry out new big interventions. Pumps for the water treatment plant that provides safe water to the city of Sheraro took six months to be replaced. During that time, the city survived thanks to deliveries made by truck or donkeys. In addition, MSF provided up to 1.4 million liters of safe water for six displacement camps each day.
Where water utility technicians are not available, MSF technicians carry out the rehabilitation directly, while training new staff hired by the water administration. The objective is to act as a catalyst in the re-activation of the pre-existing public hand pump repair system.
As recovery continues, more resources and efforts will still be required to increase the availability of safe water and improve overall sanitation and hygiene conditions in parts of Tigray.


From left: MSF built supplementary latrines for cholera patients at Sheraro health center; women wait for their children to be vaccinated at Adi Asser Health post. Ethiopia 2023 © Gabriella Bianchi/MSF
About MSF in Ethiopia
MSF has been working in Ethiopia for 37 years, providing medical assistance to people affected by conflict, epidemics, disasters or with limited access to healthcare, in collaboration with Ethiopian authorities at local, regional, and national levels. Currently, we are working in seven regions in Afar, Amhara, Gambella, Oromia, SNNP, Somali Region, and Tigray. We have been providing kala azar care for more than 20 years, including our dedicated kala azar and snakebite project in Abdurafi, Amhara, and through emergency interventions. All our activities are guided by humanitarian principles humanity, independence, neutrality, and impartiality.
On June 24, 2021, our colleagues María Hernández Matas, Tedros Gebremariam Gebremichael, and Yohannes Halefom Reda were brutally and intentionally killed while clearly identified as humanitarian workers in Tigray. After extensive engagement with Ethiopian authorities, we still do not have any credible answers on what happened to our colleagues that day. MSF will continue to use all possible means and avenues to pursue accountability for their deaths. With that, we also hope that this will contribute to improving the safety of humanitarian workers in Ethiopia.